Describe the role of polymerase in transcription. RNA polymerase I Pol I used to produce the large ribosomal subunit.

Rna Polymerase Overview Role In Transcription Expii
RNA polymerase III catalyzes the transcription of tRNA precursors in the nucleus.

. Five subunits α α β β and σ make up the complete RNA polymerase holoenzyme. These repeats contain serine and threonine residues that are phosphorylated in. Transcription and mRNA processing.
Explain how DNA is transcribed to create an mRNA sequence. Molecular structure of RNA. This is the currently selected item.
Recognize that protein synthesis regulation ie changes in gene expression allow cells to respond to changes in the environment. RNA-seq technologies and data processing tools continue to developed at rapid pace. These RNA molecules determine the three-dimensional structure of ribosomes.
Transcription termination by RNA Polymerase II on a protein-encoding gene. For the studies describe here RNA-seq was performed on Illumina HiSeq 2500 and we have used the following data analysis pipeline. In the case of protein-encoding genes a protein complex will bind to two locations on the growing pre-mRNA once the RNA Polymerase has transcribed past the end of the gene.
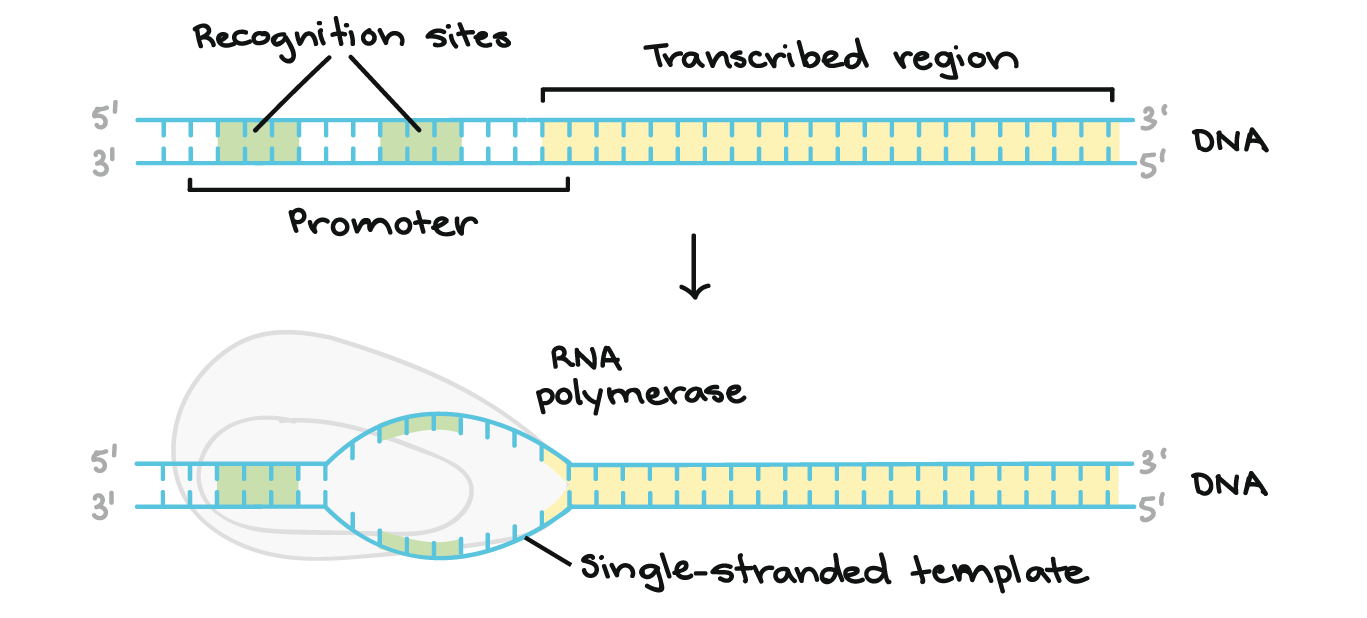
Prokaryotic rRNA is of three types and eukaryotic ribosomes are made of four types of rRNA with the largest one containing over 5000 nucleotides. RNA polymerase copies the genectic instructions to form a strand of mRNA. Two promoter consensus sequences are at the -10 and -35 regions upstream of the initiation site.
In eukaryotic cells the genome is housed in. The product of this gene contains a carboxy terminal domain composed of heptapeptide repeats that are essential for polymerase activity. Paired-end RNA-seq reads were trimmed of any adaptor sequences with the FASTX-Toolkit version 0014.
How do each of them interact with the other polymerase subunits and with. RNA consists of ribose nucleotides nitrogenous bases appended to a ribose sugar attached by phosphodiester bonds forming strands of varying. Proceedings of the.
Transcription of mRNA begins at the initiation site. They contact 7090 base pairs of DNA in promoter regions used to initiate DNA transcription during which DNA wraps around the polymerase. Remember that transcription is the process that creates RNA from DNA using RNA polymerase in all living organisms.
Because many identical RNA copies can be made from the same gene and each RNA molecule can direct the synthesis of many identical protein molecules cells can synthesize a large amount of protein rapidly when necessary. Describe the roles of the different subunits of the Ecoli RNA polymerase. This is the currently selected item.
Transcription and RNA processing. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome subunit. Transcription and translation are the means by which cells read out or express the genetic instructions in their genes.
Transcription and mRNA processing. RNA polymerase II Pol II used to produce the. Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation.
DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation. Ill break down transcription translation and the key players in the process of making protein. This gene encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes.
Learn about the steps of protein synthesis in this video. RNA polymerases are large multi-subunit complexes. RNA Polymerase II has no specific signals that terminate its transcription.
RNA polymerase unwinds the two DNA strands. But each gene can also be. Molecular structure of RNA.
Although transcription is defined principally as the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template in this Review we use the term to describe the synthesis of sg-mRNAs from RNA templates to conform with. The σ subunit of RNA polymerase recognizes and binds the -35 region. Explain the processes necessary for transcription to begin.
Eukaryotes have three different types of RNA polymerases. The mRNA carries the genetic instructions through the nuclear por complex into the cytoplasm to a ribosome subunit. Going from DNA to mRNA.
RNA abbreviation of ribonucleic acid complex compound of high molecular weight that functions in cellular protein synthesis and replaces DNA deoxyribonucleic acid as a carrier of genetic codes in some viruses. A key component the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RdRp also known as nsp12 catalyzes the synthesis of viral RNA and thus plays a central role in the replication and transcription cycle of COVID-19 virus possibly with the assistance of nsp7 and nsp8 as cofactors. A polyA addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene.

Rna Polymerase Function And Definition Technology Networks
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

0 Comments